前言 AOP是Spring中的核心功能之一,使用AOP,可以让关注点代码与业务代码分离,并且动态地添加和删除在切面上的逻辑而不影响原来的执行代码,从而可以在不修改源代码的情况下,实现对功能的增强。
AOP的应用场景很多,日志记录、性能监控、事务管理等都可以通过AOP去实现。
AOP的原理就是动态代理,在 Spring 中,存在两种实现机制, JDK 动态代理以及 CGLIB 动态代理。
在Spring Boot中,AOP可以通过**@EnableAspectJAutoProxy**注解开启,那该注解是怎么起作用的呢,代理对象又是如何被创建的呢?
以下内容基于Spring Boot 2.1.9.RELEASE版本
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class) public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy { boolean proxyTargetClass () default false boolean exposeProxy () default false }
该注解@Import了AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar 这个类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions ( AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry); AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class); if (enableAspectJAutoProxy != null ) { if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass" )) { AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry); } if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy" )) { AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry); } } } }
由类注释可以看出,AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar 的作用是向IOC容器注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 。那么AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 是什么呢?
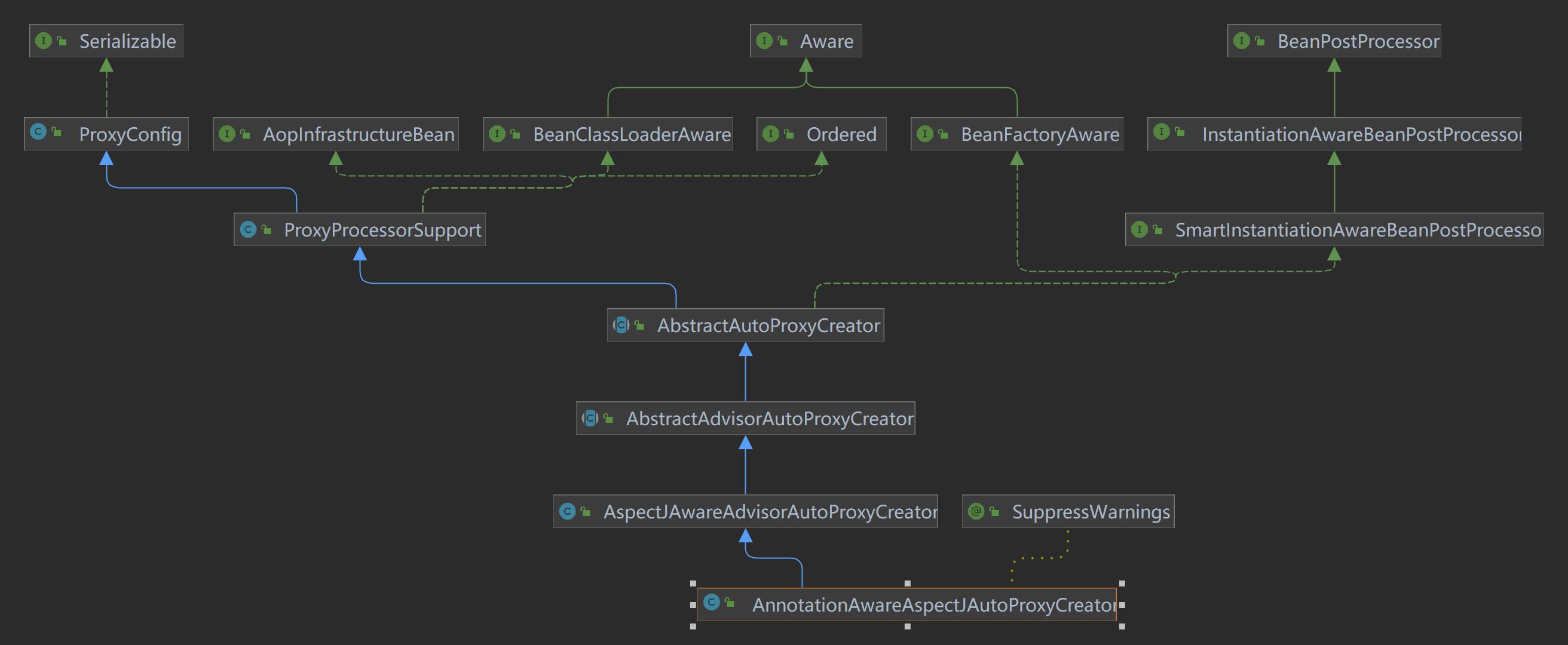
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 我们先来看下AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 的类继承关系图:
可以发现,AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator :
实现了BeanPostProcessor **接口,其关键方法 postProcessBeforeInitialization和 postProcessAfterInitialization将会在bean创建过程中的初始化流程中 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean被调用,而AOP代理代理对象也是通过 postProcessAfterInitialization**得到;
实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 接口,其关键方法postProcessBeforeInstantiation 会在bean实例化前尝试被调用;
实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 接口,其关键方法getEarlyBeanReference 将会作为提前暴露代理对象的入口放入bean的三级缓存中;
在本文中,我们主要关注postProcessAfterInitialization **方法,该方法在 AbstractAutoProxyCreator**中被实现。
AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization (@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) if (bean != null ) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); if (this .earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) { return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; }
earlyProxyReferences 查看其引用,可以发现只在getEarlyBeanReference 中被使用,而getEarlyBeanReference 是在循环引用发生的情况下被调用,结合这里的判断不难看出,这里主要是防止代理对象的重复生成。
wrapIfNecessary 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 protected Object wrapIfNecessary (Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this .targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this .advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this .advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null ); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this .advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this .proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this .advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
shouldSkip 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 protected boolean shouldSkip (Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) { if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor && ((AspectJPointcutAdvisor) advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) { return true ; } } return super .shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors () List<Advisor> advisors = super .findCandidateAdvisors(); if (this .aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null ) { advisors.addAll(this .aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors()); } return advisors; }
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean( Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) { List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName); if (advisors.isEmpty()) { return DO_NOT_PROXY; } return advisors.toArray(); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors (Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; }
createProxy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 protected Object createProxy (Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) if (this .beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) { AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this .beanFactory, beanName, beanClass); } ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(); proxyFactory.copyFrom(this ); if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) { if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) { proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true ); } else { evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory); } } Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors); proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors); proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource); customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); proxyFactory.setFrozen(this .freezeProxy); if (advisorsPreFiltered()) { proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true ); } return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader()); }
getProxy 创建代理对象:
1 2 3 public Object getProxy (@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy () if (!this .active) { activate(); } return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this ); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public AopProxy createAopProxy (AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) { Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null ) { throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " + "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation." ); } if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config); } else { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } }
最终来到DefaultAopProxyFactory,然后是我们熟悉的逻辑:
如果目标对象有接口,用JDK动态代理;
如果没有接口,用CGLIB动态代理;
总结
AOP代理对象的创建通过AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 实现,该类是BeanPostProcessor 的子类,并且在不存在循环依赖的情况下,是在postProcessAfterInitialization 方法中创建的;
postProcessAfterInitialization 中,会匹配出所有和当前Bean相关的增强器,并最终根据实际情况判断是使用JDK动态代理,还是CGLIB动态代理;